
Brief remark on VAE
\[\begin{align} \mathcal{L}(\theta,\phi;x^{(i)}) & = \mathbb{E}_{q_\phi(z\lvert x)}{[ -\log q_\phi (z \lvert x) + \log p_\theta (x,z) ]} \\ & = \mathbb{E}_{q_\phi(z\lvert x)}{[ \log p_\phi (x \lvert z)]} - KL(q_\phi(z\lvert x) \lvert \lvert p(z)) \end{align}\]Main Contributions
- Motivation
- Lauguage는 그 특성상 inherently discrete하며, Image도 Language로 describe할 수 있기에 image도 discrete encoding(embedding)을 할 수 있다고 볼 수 있다.
- Introduce a new family of generative models succesfully combining the VAE framework with discrete latent representations through a novel parametrization of the posterior distribution of (discrete) latents given an observation.
- VQ-VAE is simple to train, does not suffer from large variance, and avoids the “posterior collapse” issue
- Decoder $p_\theta(x\lvert z)$가 Powerful한 경우 latents가 무시된다.
- 위의 (2)번식을 보면 Decoder $p_\theta(x\lvert z)$가 있는 부분이 첫번째 term인 reconstruction term인 것을 알 수 있다.
- 다시 말해 각 $x$에 따라 $z$가 적당히 다르게만 encode되면(다시 표현하면 $x$의 intrinsic manifold특성이나 내부의 숨겨진 특징이 확률분포처럼 뭔가 meaningful한 것으로 encode되지 않고 그냥 아무 semantic이 반영되지 않는 z로 encode된다면) powerful decode가 그냥 $z$를 외워 그 $z$에 대응되는 $x$만 decode하는 방식으로 위의 (1), (2) ELBO식을 충분히 크게 Maximize 할 수 있다.
- 즉, ELBO를 크게 하는 목표를 달성하지만 우리가 원하는 encode부분($q_\phi(z\lvert x)$)은 망할 수 있다는 것이다.(이를 “posterior collapse”라 하는 듯!)
- VQ-VAE는 latent spacef를 effectively 사용한다.
- Powerful Prior를 통해서 high quality하고 coherent한 이미지,스피치, 비디오 생성을 할 수 있다.(특히 raw speech에서 supervision없이 unsupervised speaker conversion을 해냈다)
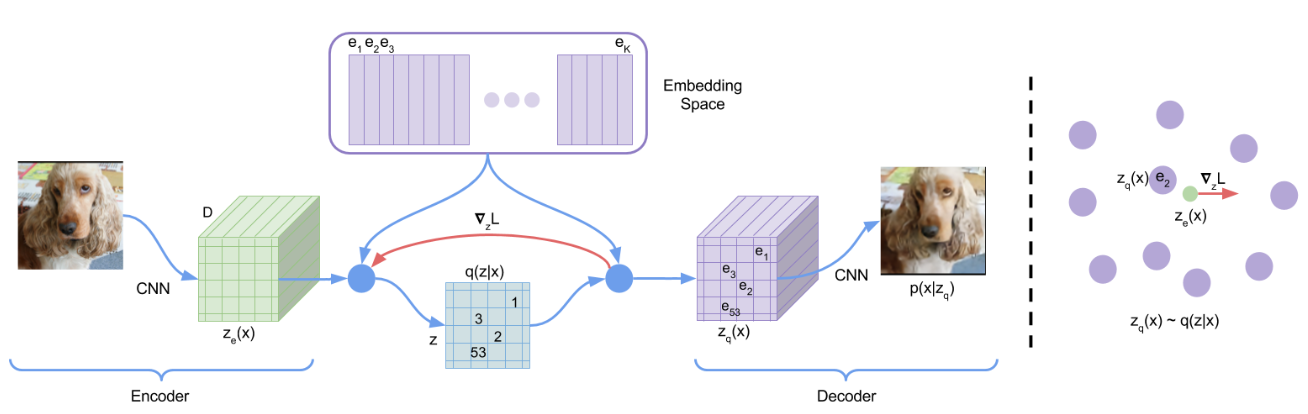
VQ-VAE
- The posterior and prior distributions are categorical, and the samples drawn from these distributions index an embedding table.
- These embeddings are then used as input into the decoder network.
Notations
- $e\in \mathbb{R}^{K\times D}$, $K$: the size of the discrete latent space, $D$: the dimension of each latent embedding vector $e_i$.
Discrete Latent variables
\[q(z=k\lvert x)= \begin{cases} 1 \quad \text{for } k=\text{argmin}_j \lvert\lvert z_e(x) -e_j\lvert\lvert_2, \\ 0 \quad \text{otherwise}\end{cases}\] \[z_q(x)=e_k, \quad \text{where} \quad k=\text{argmin}_j \lvert\lvert z_e(x) -e_j\lvert\lvert_2\]KL term in VAE?
KL term은 (2)식에서 보이는 것처럼 $KL(q_\phi(z\lvert x) \lvert \lvert p(z)) $인데 VQ-VAE에서는 보이지 않는다. 논문에서는 이 값이 상수($\log K$)라고 하는데 이는 간단히 보일수 있다. 먼저 prior $p(z)$가 논문에서 uniform categorical distribution이라고 뒀다는 걸 생각하면 discrete output $i=1,\cdots,K$ 각각에 대하여 모두 $p(z=i)=\frac{1}{K}$임을 생각하자. 또한 $q_\phi(z=k\lvert x)$가 위의 식에서 보이는 것처럼 argmin인 $z=k$에서만 1의 확률을 갖고 나머지 $z\neq k$에 대해서는 0의 확률을 갖는 one hot느낌의 categorical distribution을 갖는 posterior distribution임을 추가로 고려하면 다음과 같이 KL term이 계산된다.
\[KL(q_\phi(z\lvert x) \lvert \lvert p(z)) = \sum_{z=1}^K q_\phi(z\lvert x) \log (q_\phi(z\lvert x) / p(z)) = 1*\log (1/(\frac{1}{K}))=\log K\]Learning
\[L = \log p(x\lvert z_q(x))+\lvert\lvert sg[z_e(x)]-e\lvert\lvert_2^2+\beta \lvert\lvert z_e(x)-sg[e]\lvert\lvert_2^2\]Prior
먼저 prior $p(z)$를 uniform categorical distribution으로 고정해놓고 VQ-VAE의 모델을 학습시킨 다음에, Autoregressive model(e.g. PixelCNN, WaveNet)을 이용하여 p(z)를 autoregressive distribution이 되게 바꾼다음에 학습을 한다. 이때 $z$로 부터 $x$를 sampling(generate)할 때 ancestral sampling이 사용된다.
Conclusion
- VAEs with vector quantization to obtain a discrete latent representation
- VQ-VAEs are capable of modelling very long term depedencies through their compressed discrete latent space
- can model long range sequences and fully unsupervised learn high-level speech decriptors that are closely related to phonemes
If you like this post, don’t forget to give me a star. ![]()
