Abstract
정보이론을 사용하여 unsupervised하게 disentangled representation을 배울 수 있는 GAN기반 모델을 제안하였다. InfoGAN은 observation과 latent code의 일부 집합의 mutual information을 높이고자 하였다. 이 과정에서 mutual information의 lower bound를 유도하였고 이를 효과적으로 최적화할 수 있는 방법도 제안하였다. 이를 통해 MNIST, 3D rendered pose images from various lighting, SVHN datatset에 대하여 disentangle되는 걸 보여주었다. CelebA 데이터에 대해서는 특별히 머리스타일, 안경유무, 감정 등에 대한 representation을 discover하였다. Existing supervised methods와 비교해서도 실험결과 측면에서 꿀리지 않는 interpretable representation 결과를 보여주었다.
Adversarial nets
\[\min_{G} \max_{D} V(D,G)=\mathbb{E}_{x\sim p_{\text{data}}(x)}[\log D(x)] + \mathbb{E}_{z\sim p_z(z)}[\log D(G(z))]\]Mutual Information for Inducing Latent Codes
\[P(c_1,\cdots c_L)=\prod_{i=1}^L P(c_i)\]Information-regularized minimax game
\[\min_G \max_D V_I(D,G) = V(D,G)-\lambda I(c;G(z,c))\]Variational Mutual Information Maximization
Mutual information term $I(c;G(z,c))$이 directly maximize하기 어렵다. 이유는 posterior $P(c\lvert x)$를 access해야하기 때문이다.
posterior가 intractable하기 때문에 이를 해결하기 위해 VAE에서 했던 거처럼 Variational approach를 사용한다. 즉 $P(c\lvert x)$ 대신에 $Q(c\lvert x)$를 도입한다. 이렇게 도입함으로 인해 다음의 부등식이 유도된다.
\[\begin{align*} I(c;G(z,c))&=H(c)-H(c\lvert G(z,c)) \\ &=\mathbb{E}_{x\sim G(z,c)} [ \mathbb{E}_{c'\sim P(c\lvert x)}[\log P(c'\lvert x)] ]+H(c) \\ &=\mathbb{E}_{x\sim G(z,c)} [KL(P(\cdot \vert Q(\cdot \lvert x))+\mathbb{E}_{c'\sim P(c\lvert x)}[\log Q(c' \lvert x]]+H(c) \\ &\geq \mathbb{E}_{x\sim G(z,c)}[\mathbb{E}_{c'\sim P(c\lvert x)}[\log Q(c'\lvert x)]]+H(c) \end{align*}\]Lemma 5.1 For random variables $X,Y$ and function $f(x,y)$ under suitable regularity conditions:
\[\mathbb{E}_{x\sim X, y\sim Y\lvert x} [f(x,y)] = \mathbb{E}_{x\sim X, y\sim Y\lvert x, x'\sim X\lvert y} [f(x',y)]\]Also,
\[L_I(G,Q)=\mathbb{E}_{x\sim G(z,c)}[\mathbb{E}_{c'\sim P(c\lvert x)}[\log Q(c'\lvert x)]]+H(c) \leq I(c;G(z,c))\]- Note that $L_I(G,Q) is easy to approximate with Monte Carlo simulation.
- In particular, $L_i$ can be maximized w.r.t. $Q$ directly and w.r.t. $G$ via the reparametrization trick.
- Hence, $L_I(G,Q)$ 가 기존 GAN objective에 더해져서 훈련할 수 있음. 이걸 InfoGAN이라 부르자.
결국 InfoGAN은 다음의 Minimax game with a variational regularization of mutual information and a hyperparameter $\lambda$
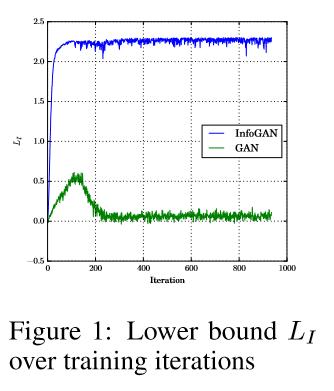
\[\min_{G,Q} \max_{D} V_{\mathrm{InfoGAN}}(D,G,Q) = V(D,G)-\lambda L_I(G,Q)\]Experiments


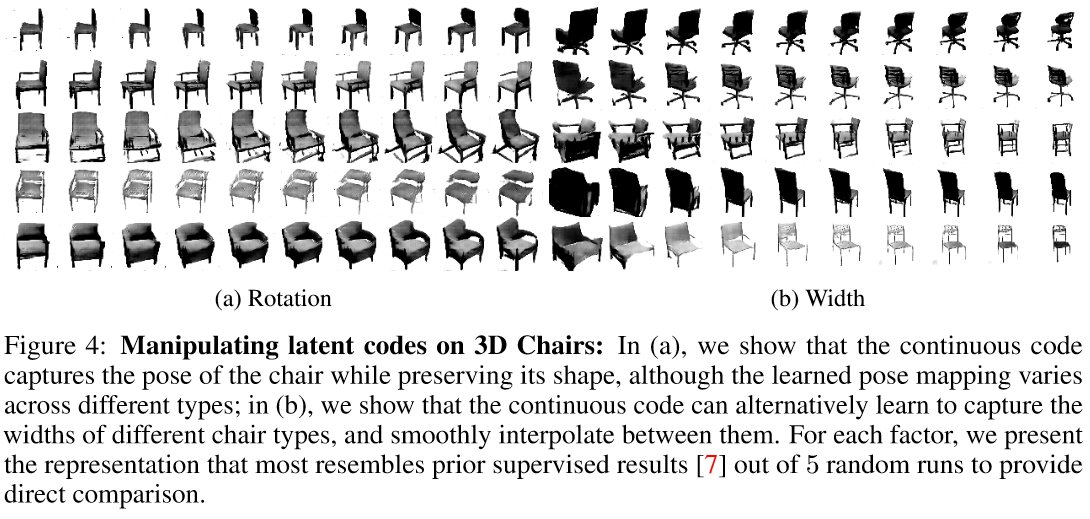
Conclusion
InfoGAN은 previous approach와 르게 supervision없이 interpretable and disentangled representation을 challenging dataset들에 대해서 배울 수 있었다. 특히 GAN에 특별히 추가되는 computation cost가 많지 않으면서 그대로 훈련할 수 있다.
If you like this post, don’t forget to give me a star. ![]()
